
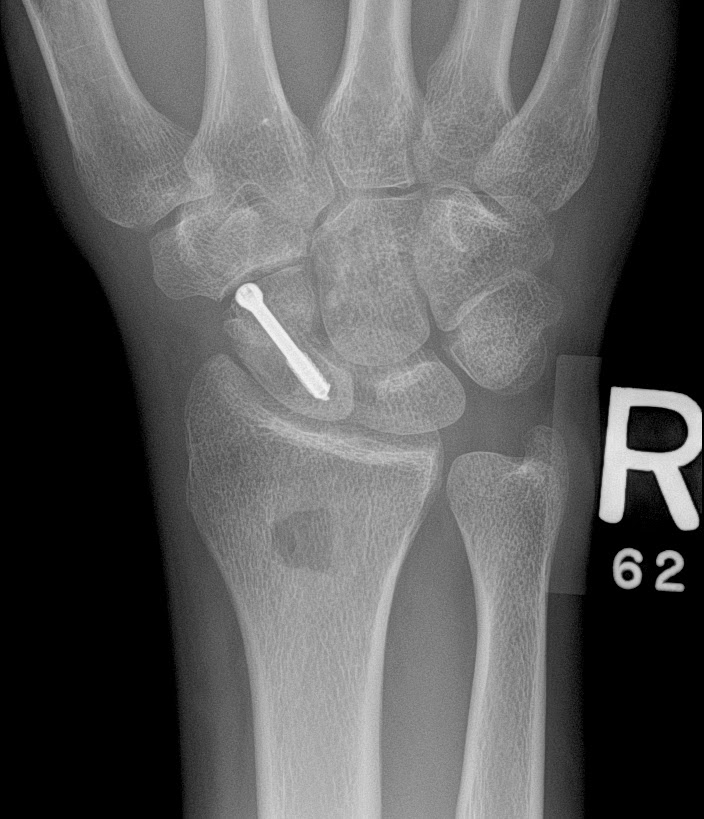
These forces initially cause a bone stress reaction and continuous damage. Like all the other stress fractures, this overuse injury is a result of excessive and repetitive compressive forces that act on it during the weight bearing process. A navicular fracture is a break in the navicular bone on the top of the midfoot.
Navicular fracture crack#
All stress reactions and stress fractures of the navicular that are managed non-operatively need at least 6-8 weeks of strict non-weight bearing due to the high risk of delayed healing and non-union. Navicular stress fracture is an injury marked by an incomplete crack in one of the mid-foot bones. Caution also must be exercised in managing navicular dislocations because of the potential long-term complications of redislocation or painful flatfoot deformity if alignment is not maintained. Navicular stress fractures can be managed non-operatively initially but there are some that do better with immediate surgical management. Early postoperative range of motion, prolonged protected weight bearing, and aggressive patient counseling as to the severity and long-term implications of these injuries also are paramount to success.
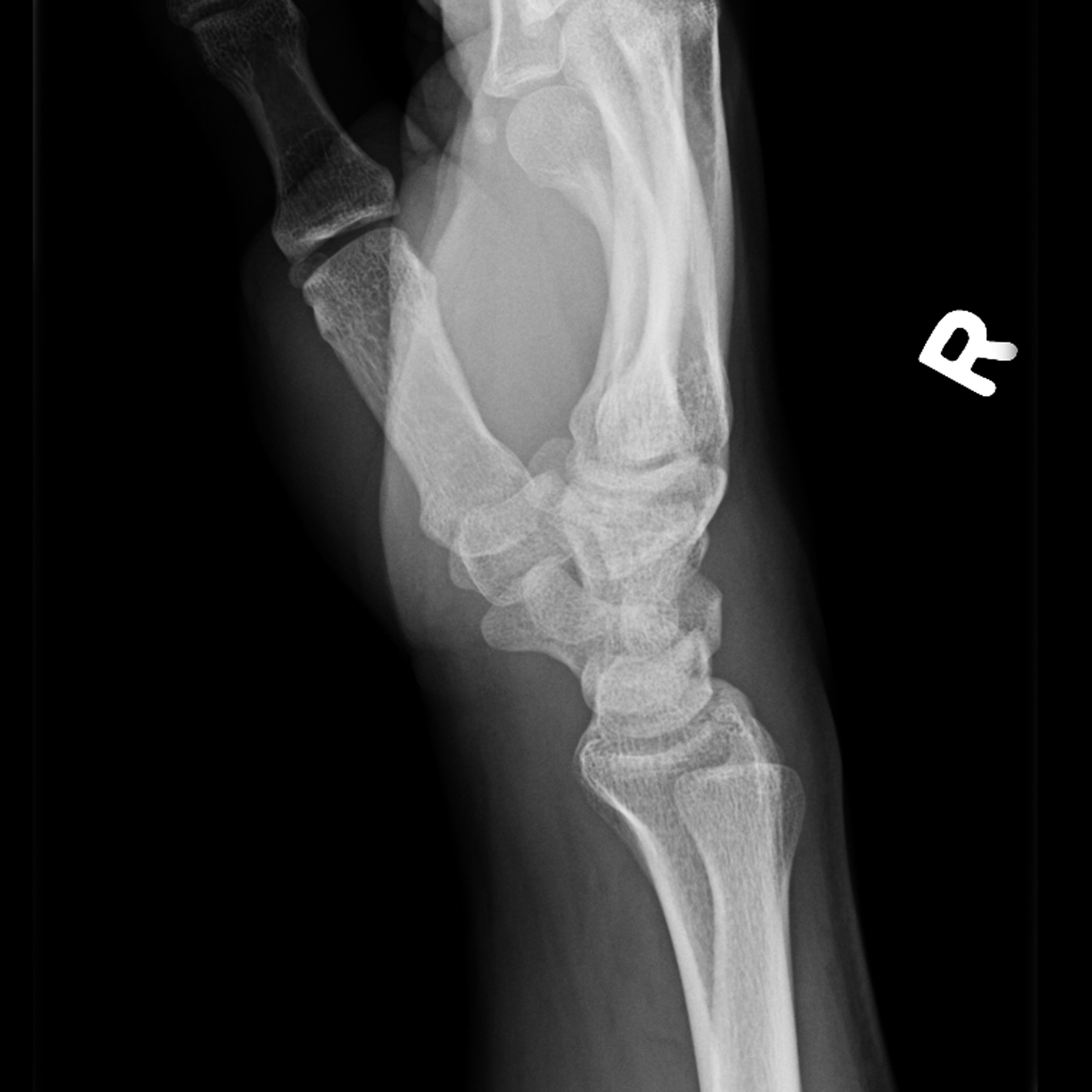
External fixation, bone grafting (often and early), and limited peritarsal fusion also have evolved into useful aids, under certain circumstances, to facilitate the goals of navicular fracture management. The naviculo-cuneiform joint, alternatively, requires stability for proper foot function and can be fused, if necessary, to improve fixation or enhance vascularity to the navicular. The likelihood for successful reduction decreases with increasing grades of injury. The unique morphology and vital role of the navicular as a cornerstone of the talonavicular joint require every effort to maintain the congruity and motion of this joint to avoid later fusion. Stress fractures occur when an individual. Open reduction and internal fixation of these injuries allow anatomic restoration of adjacent joint surfaces and preservation of length and stability along the medial column of the foot intervention must not disrupt the already tenuous blood Supply of the tarsal navicular because of the associated risks of avascular necrosis and nonunion. The most common cause of a navicular fracture is overuse this type of injury is also known as a stress fracture. Generally, large or significantly displaced intra-articular navicular fractures are treated best by surgical intervention.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
